Melting and Boiling Points
Cesium has an extremely low melting point of only 28.44°C, making it one of the metals with the lowest melting points. Its boiling point is also relatively low, at around 671°C. This low melting point means that cesium easily becomes liquid at slightly elevated temperatures, giving it advantages in special low-temperature applications or scenarios where low melting points are required.
Density and Hardness
Cesium has a density of approximately 1.879 g/cm³, which is relatively low. It also has an extremely low hardness, with a Mohs hardness of only about 0.2. It is very soft and can easily be cut with a knife and pressed into thin sheets.
Ductility and Electrical Conductivity
Cesium has a certain degree of ductility, but due to its softness, its practical applications in this regard are somewhat limited. It is an excellent conductor of electricity, with a high electrical conductivity that allows it to effectively conduct electric current. This makes it valuable in applications where electrical conductivity is required.
Oxidation State and Reactivity
The common oxidation state of cesium in compounds is +1. It is extremely reactive chemically and is highly susceptible to oxidation in air. It reacts violently with oxygen and water, forming cesium hydroxide and other compounds, often accompanied by combustion and explosive phenomena. Therefore, special measures such as sealing and air isolation are usually required to store cesium.
Reaction with Acids and Bases
Cesium reacts extremely violently with acids in a displacement reaction, producing the corresponding cesium salts and hydrogen gas. The reaction is very fast and releases a large amount of heat. As an alkali metal and a strong base, cesium does not undergo conventional chemical reactions in alkaline solutions but exists in ionic form.
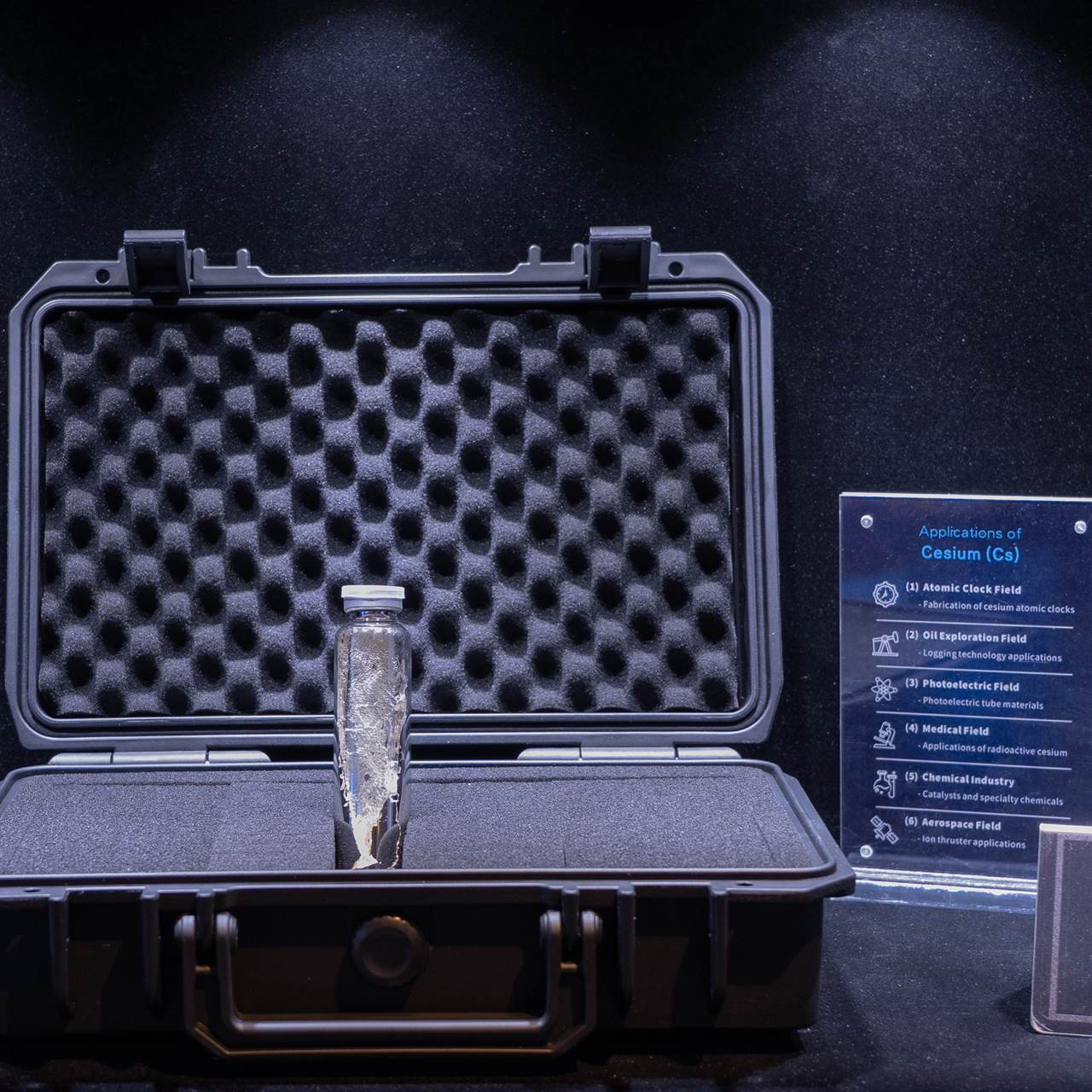
Atomic Clock Field
Manufacturing Cesium Atomic Clocks
One of the most important applications of cesium is in the manufacturing of cesium atomic clocks. Cesium atomic clocks are among the most precise timekeeping instruments in the world. They use stable frequency corresponding to specific energy level transitions in cesium atoms for timekeeping. Their accuracy can reach an error of no more than 1 second in 100 million years. They play a key role in various fields requiring high-precision time measurement, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), aerospace navigation, time synchronization in communication networks, and fundamental scientific research. They ensure the precision of all spatiotemporal-related information.
Petroleum Exploration Field
Application in Logging Technology
In petroleum exploration, cesium compounds (such as cesium formate) are used as logging fluids. Due to their high density, good solubility, and relatively good chemical stability, cesium compounds can better transmit pressure, temperature, and other information in the complex geological environment downhole. This helps staff accurately understand the conditions of underground oil layers, improving the accuracy and efficiency of petroleum exploration.
Photoelectric Field
Photoelectric Tube Materials
Cesium has excellent photoelectric effect characteristics and is highly responsive to light. Therefore, it can be used as a key material in photoelectric conversion devices such as photoelectric tubes. Under light exposure, cesium can quickly release electrons, efficiently converting light energy into electrical energy. It is applied in fields such as light signal detection, automatic control, and photographic lighting. For example, early photoelectric detectors and photoelectric conversion components in movie projectors used cesium-related materials to achieve photoelectric conversion functions.
Medical Field
Application of Radioactive Cesium
Certain radioactive isotopes of cesium (such as cesium-137) have certain applications in medicine. For example, in radiotherapy, cesium-137 can be used to kill cancer cells after strict control and precise positioning, treating some types of tumors. Additionally, in medical imaging, its radioactive properties can be used to assist in observing the function and pathological conditions of internal body tissues. However, the use of radioactive cesium must strictly follow relevant safety regulations to prevent radiation hazards.
Chemical Industry
Catalysts and Specialty Chemicals
In some chemical reactions, cesium compounds can be used as catalysts. For example, in organic synthesis reactions and polymerization reactions, cesium salts can accelerate the reaction process, improve reaction selectivity, and enhance product quality. Additionally, cesium can be used to produce some specialty chemicals to meet the demand for special chemical substances in specific industrial fields.
Aerospace Field
Application in Ion Thrusters
In the aerospace field, cesium can be used as a propellant for ion thrusters. Ion thrusters generate thrust by ionizing atoms such as cesium and accelerating them for ejection. Although this propulsion method has relatively low thrust, it has a higher specific impulse (i.e., the impulse generated per unit of propellant) than traditional chemical propellants. It can provide continuous propulsion for spacecraft over long space missions, improving the efficiency and mission capabilities of spacecraft.